Prior-Guided Infrared Spatiotemporal Noise Modeling Based on Hybrid Neural Representation
Jan 22, 2026··
0 min read
Chao Qu
Abstract
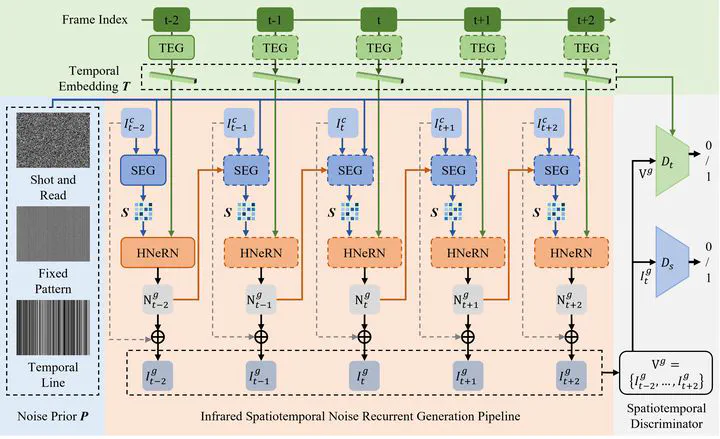
Noise modeling of imaging sensors is a critical challenge in infrared vision applications. Existing noise modeling methods primarily focus on the spatial distribution, making it difficult to accurately characterize the temporal variations of infrared noise in dynamic scenes, thereby limiting the performance of video denoising algorithms. To address this problem, we construct an infrared video dataset that contains real indoor and outdoor scenes for noise modeling and algorithm evaluation. Based on this, we propose IRSTN, an infrared spatiotemporal noise modeling framework, that synthesizes high-fidelity noise from unpaired data. Specifically, IRSTN incorporates noise priors to generate spatial embeddings capturing noise spatial context, and employs position encoding of frame indices to produce temporal embeddings representing noise temporal correlations. Furthermore, IRSTN develops a hybrid neural representation of noise that deeply integrates spatial and temporal embeddings, implicitly modeling the spatiotemporal noise distribution via recurrent adversarial learning. Quantitative evaluations demonstrate that the infrared noise generated by IRSTN exhibits high consistency with real noise in spatiotemporal characteristics. Extensive denoising experiments show that IRSTN significantly improves the performance of video denoising networks in real-world scenes.
Type
Publication
Optics Express